Developmental Skills
Developmental Skills
Fine Motor
Fine motor skills are small, precise movements using the muscles in hands and wrists. Fine motor skills include grip/hand strength, pincer grasp, in-hand manipulation, motor planning, crossing midline, calibration/force control, and bilateral coordination. These skills are used for many occupations and tasks such as holding and manipulating objects, dressing, self-care, and writing.
The charts below display the therapeutic benefits and development skills promoted by each art activity.
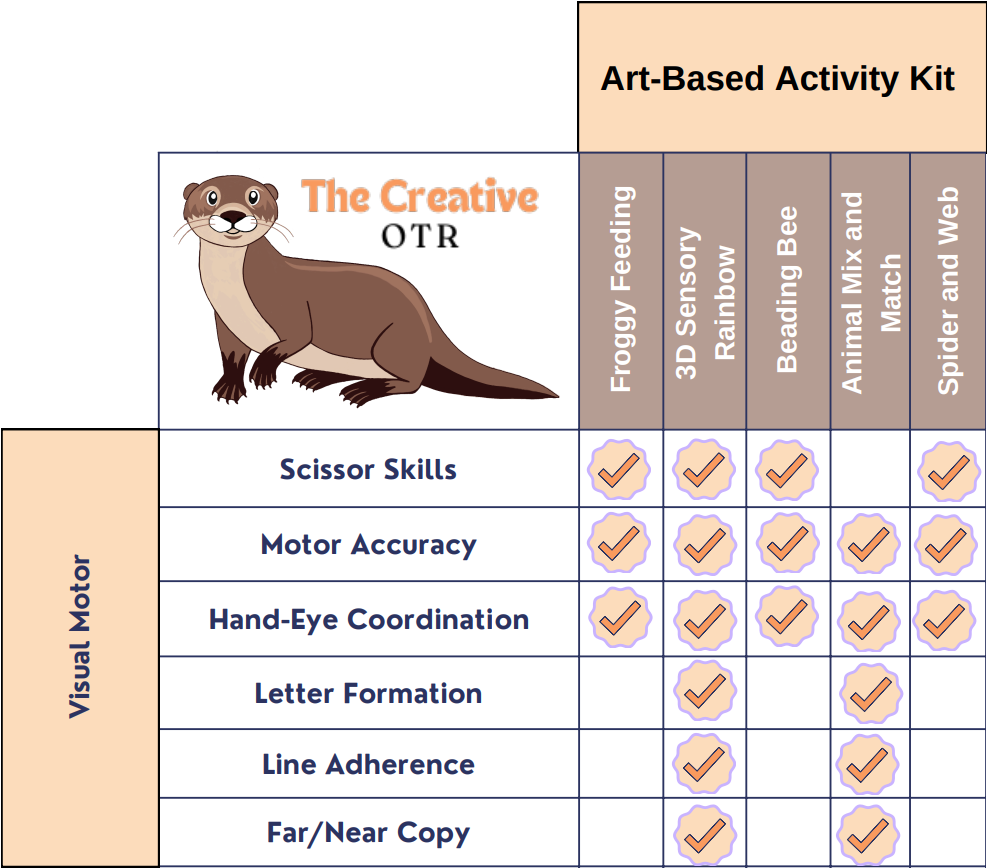
Visual Motor
Visual motor skills are characterized by coordinating visual perception and fine motor skills. Visual motor skills include scissor skills, motor accuracy, hand-eye coordination, letter formation. These skills are used for many occupations and tasks such as writing, copying from board or desk, reading, dressing, and self-care.
Visual Perception
Visual perception is the interpretation of visual information. Visual motor skills include visual attention, visual memory, visual spatial relationship, visual figure ground, visual form constancy, and visual closure. These skills are used for many occupations and tasks including focusing, recalling visual information, spelling, writing, reading, puzzles, navigating environment, recognizing and finding objects, and following directional terms.
Gross Motor/Postural
Gross motor skills and posture use large muscles for control, balance, and coordination. Gross motor skills include shifting weight, bilateral coordination, balance, proximal stabilization, core strength, and motor planning. These skills are used for many occupations and tasks such as reaching for objects, playing/climbing on playground equipment, using stairs, stressing, sitting upright in a chair, changing positions, running, jumping, kicking/throwing/bouncing balls, and self care.
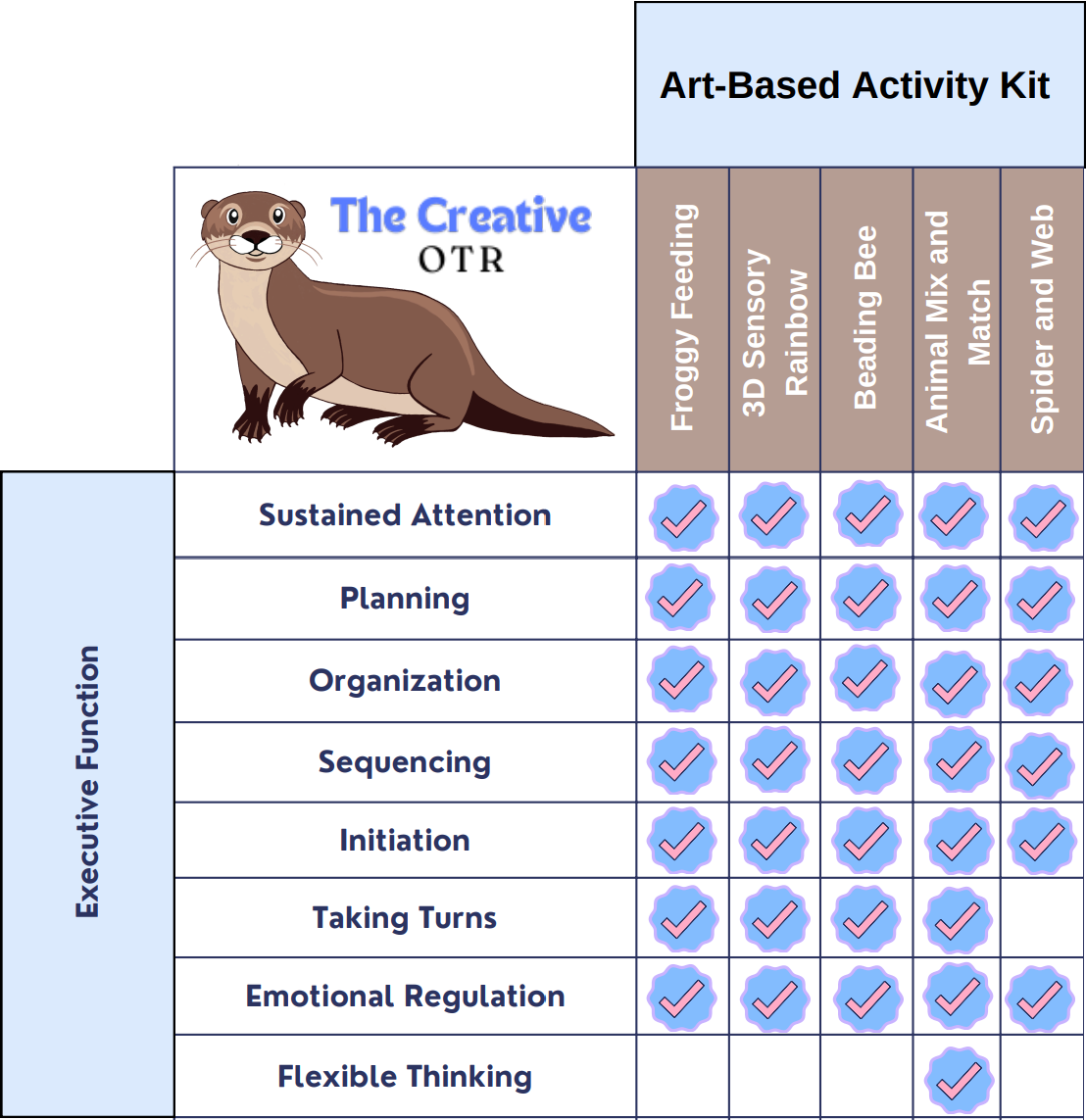
Executive Function
Executive function is cognitive processing skills to enhance development and knowledge needed to make decisions, plan, and carryout the plan. Executive function skills include sustained attention, planning, organization, sequencing, initiation, taking turns, emotional regulation, and flexible thinking. These skills are used for many occupations and tasks such as focusing on a task while distracted, starting and completing steps of a task in the correct order, keeping desk, room, backpack clean and organized to find materials, turning homework in on time, managing time, taking turns in a conversation or activity, managing stress or difficult situations, making friends, learning a new task, and changing schedule or routine.
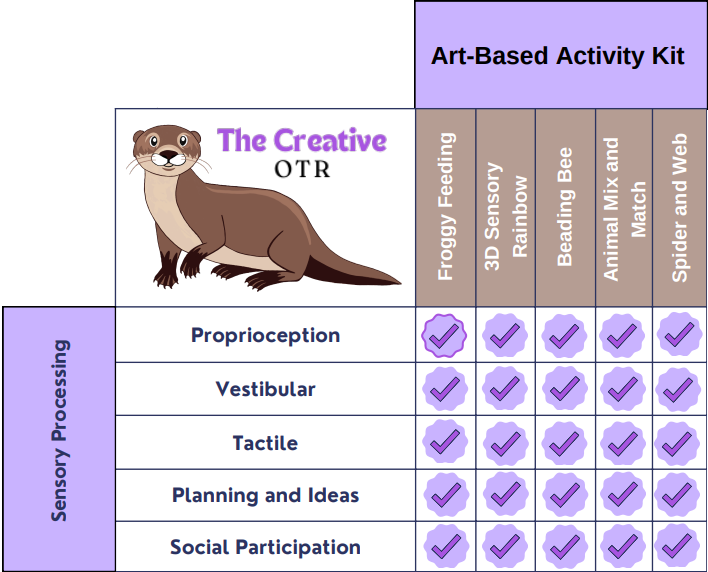
Sensory Processing
Sensory processing is how an individual receives, processes, and responds to sensory input including vision, hearing, taste and smell, tactile, vestibular, proprioception, planning and ideas, and social participation. Sensory processing is used during many occupations and tasks including navigating environment, changing body positions, writing, drawing, reading, playing, self-care, planning and organizing movements, verbal and non-verbal communication, building relationships, conflict resolution, respect, and cooperative play.